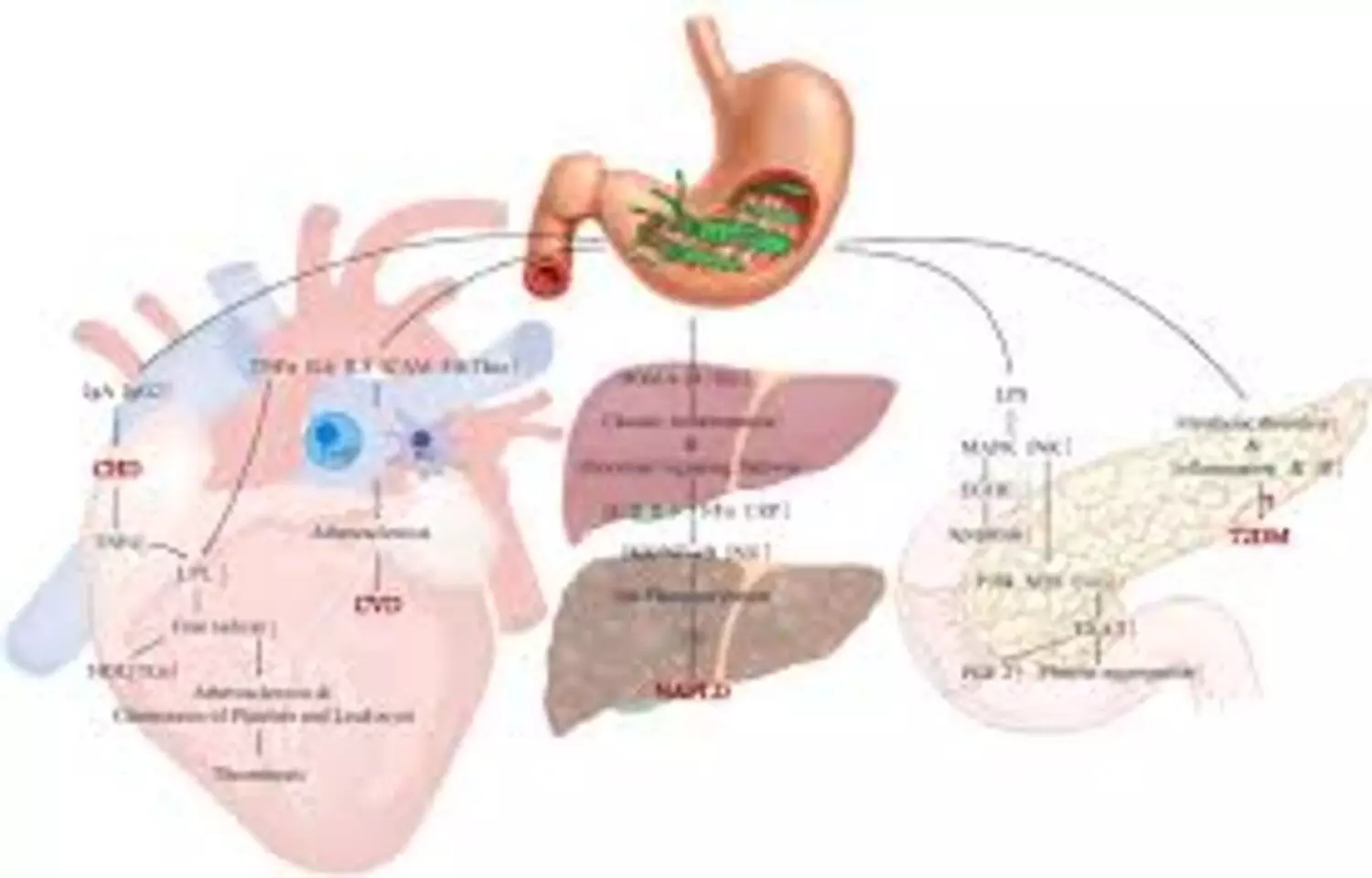
Researchers have found in a new study that H. pylori infection is associated with increased Remnant cholesterol levels, and this relationship appears to be mediated through insulin resistance and inflammatory processes.Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) represents a widespread chronic bacterial infection that has garnered increasing attention in recent years due to its extra-gastric effects. Remnant cholesterol (RC) is recognized as a non-traditional lipid marker and is a significant predictor of residual risk in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. This investigation aimed to analyze the correlation between H. pylori infection and Remnant cholesterol levels, as well as to reveal the underlying mechanisms. The study population comprised individuals undergoing routine health examinations at the health examination center of Taizhou Hospital. All participants were subjected to urea breath tests, blood tests, and anthropometric measurements. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index was utilized to assess insulin resistance (IR) levels, while the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) was utilized as an indicator of chronic inflammation levels within the population. To assess the relationship between H. pylori infection and Remnant cholesterol, a multiple linear regression analysis was carried out, also investigating the mediating roles of the TyG index and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.Results: Multiple linear regression analysis demonstrated a significant association between H. pylori infection and Remnant cholesterol levels, with this relationship being stable across diverse populations. Mediation analysis further revealed that the TyG index and erythrocyte sedimentation rate significantly mediate the relationship between H. pylori and Remnant cholesterol levels. Moreover, longitudinal analysis demonstrated that persistent H. pylori infection results in a marked increase in Remnant cholesterol levels.The research identified an association between H. pylori infection and elevated Remnant cholesterol levels, with IR and inflammation acting as mediating factors in this relationship.Reference:Chen, Y., Shen, L., You, N., & Zhang, J. (2025). Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and remnant cholesterol: The mediating role of insulin resistance and inflammation. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 15, Article 1684556. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2025.1684556Keywords:Helicobacter pylori infection, remnant cholesterol, insulin resistance, systemic inflammation, metabolic risk, dyslipidemia, cardiometabolic disease, gastric infection, clinical biomarkers, Chen, Y., Shen, L., You, N., & Zhang, J